- TOP 5 REASON TO CONSIDER THE BIOGRAVITY RPM PLATFORM FOR IN-LAB SIMULATED MICROGRAVITY
Low Cost– One-time fee enables endless experimenting and predictable costs
Faster Iterations– Desktop RPM is always there in the lab
Endless Time of Simulated Microgravity-Unlike suborbital spacecrafts (5-10 min), parabolic flights (20 s) and drop towers (9 s) unload gravity on your timetable for as long as you want.
Prepare for Flight | Reduce Variables– Duplication of expected results are far more guaranteed when you shakeout your biological experiments on the ground. Control for the effects of launch, radiation exposure, descent, and ground transport with a BioGravity platform in your own lab.
No Schedule Bumps, Military Delays or NASA Manifests-Cut through bureaucracy. It’s your experiment, deploy when you want on your own platform,
Push for Progressive Grants-Nothing sets up success like prior success. Get an early read and practical results without venturing to the heavens.
…the world’s best desktop random positioning machine (RPM)
WHAT TYPES OF RESEARCH CAN YOU DO IN YOUR LAB WITH THE EXPLOR SPACE BIOGRAVITY PLATFORM?
| FUNCTION | EXPERIMENT | SIMULATED | SPACEFLIGHT |
| GRAVITATIONAL UNLOADING | YES | YES |
| LOW EARTH ORBIT | YES | YES |
| MOON | YES | YES |
| MARS | YES | NO |
| Macrophage Differentiation | YES | YES |
| Decrease Macrophage Quantity | YES | YES |
| Decrease Functional Polarization | YES | YES |
| Metabolic Reprogramming | YES | YES |
| Alter Gene Expression Profiles | YES | YES |
| RAS/ERK/NFκB as a major microgravity-regulated pathway | YES | YES |
| Modulation of Cytokines | YES | YES |
| Motility In Microbial Behavior | YES | YES |
| Chemotaxis | YES | YES |
| Nutrient Assimilation | YES | YES |
| Tissue Localization and Invasion | YES | YES |
| Pathogenicity | YES | YES |
| Biofilm Formation | YES | YES |
| Prediction of Microbial Changes during Spaceflight | YES | NO |
| Low Fluid Shear Conditions | YES | YES |
| Shear Stress Modulation | YES | YES |
| Ground-Based Bio-Reactors | YES | NO |
| Replicate Weightlessness | YES | YES |
| Incompressable Fluid Environment | YES | YES |
| Fladgellar Assembly | YES | YES |
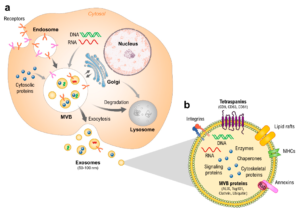
| Extracellular Vesicles | ||
| RADIATION SHEILDING | YES | NO |
| GAMMA RAY SHIELDING | YES | NO |
| SETTLING | YES | YES |
| BOUYANT CONVECTION | YES | YES |
| SPHERICAL AGGLOMORATION | YES | YES |
| CHRYSTALIZATION RESOLUTION | YES | YES |
| ENZYME PURIFICATION | YES | YES |
| Liquefaction or Hydrolysis | YES | YES |
| Epidermal Growth Factors | YES | YES |
| Inflamatory Response | YES | YES |
| Marangoni Convection | YES | YES |
| Cell Surface Interactions | YES | YES |
| Melanin UV Experiments | YES | YES |
| 3D Structure | YES | YES |
| Difraction Microscopy | YES | YES |
| Form a String of Amino Acids | YES | YES |
| Acoustic Reshaping of Bubbles | YES | YES |
| STEM CELLS | ||
| Triggers Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Human Keratinocytes | YES | YES |
| Bone Formation | YES | YES |
| Reduction of Hair Formation | YES | YES |
| Lower calcium and potassium currents | YES | YES |
| Organism Cyrcadium Rhythm in Microgravity | YES | YES |
| regeneration in µg on Platyhelminthes | YES | YES |
| cellular and physiological processes in Xenopus | YES | YES |
| Gravity Deprivation in Drosophila | YES | YES |
| PLANTS | ||
| Altering cell membrane integrity | YES | YES |
| Accumulation of hazardous substances | YES | YES |
| Affectation of Cell Nucleus Structures | YES | YES |
| frequency of mininucleolus | YES | YES |
| malondialdehyde (MDA) content | YES | YES |
| superoxide content | YES | YES |
| Changes in cell cycle, cell wall and gene expression | YES | YES |
| bioregenerative life support systems | YES | YES |
| Transcriptomics (e.g. total RNA extraction, RT-PCR and gene array) | YES | NO |
| Proteomics (e.g. mass spectrometry) | YES | NO |
| Cell viability assay (e.g. trypan blue assay) | YES | YES |
| Cell cycle assay (e.g. propidium iodide staining of cellular DNA content) | YES | YES |
| Apoptosis (e.g. annexin V – FITC detection) | YES | NO |
| Quantitative protein detection (e.g. Western Blot of protein(s) of interest) | YES | NO |
| Quantitative protein detection (e.g. immunocytochemistry) | YES | NO |
| Transcriptional Level Alterations (e.g. qRT-PCR) | YES | YES |
| Post-Transcriptional Level Alterations(e.g. proteomics, cellular markers) | YES | YES |
| Cancer-Relevant Cellular Processes | ||
| Cell Cycle | YES | YES |
| Proliferation | YES | YES |
| Apoptosis | YES | YES |
| Cellular morphology (cytoskeleton) | YES | YES |
| Adhesion (extra-cellular matrix) | YES | YES |
| Migration | YES | YES |
| Two-dimensional monolayer | YES | YES |
| Three-dimensional aggregates (Spheroids) | YES | YES |
| Spheroid formation in metastasis | YES | YES |
| Cell Matrix and Pathway Growth | ||
| Signalling Pathways | YES | YES |
| Extracellular Matrix | YES | YES |
| Focal Adhesion | YES | YES |
| Stem Cell & Regenerative Medicines | ||
| Osteoblast | YES | YES |
| Tissue | YES | YES |
| Cartilage | YES | YES |
| Biological Mineralization | YES | YES |
| Microbiology | ||
| Pro- and Eukaryotes | YES | YES |
| Pathogens | YES | YES |
| Pseudomonas Aeruginosa | YES | YES |
| Candida Albicans | YES | YES |
| Waste Recylcing | ||
| Rhodospirillum Rubrum | YES | YES |
| Organism Modeling | YES | YES |
| S. Cerevisiae | YES | YES |
| Paramecium | YES | YES |
| Quorum Sensing | YES | YES |
| Photosynthetic Systems | YES | YES |
| Gene Expression | YES | YES |
| Production of Pigments | YES | YES |



More Stories
UCSD Sends Blood Stem Cells to Space